Automation has become essential in many fields of industries. It allows processes to function with increased efficiency and productivity. Today's industrial automation is leveling to the next stage of the industrial revolution with the innovation of breakthrough technology such as artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, the Internet of Things, robotics, and others.
What is industrial automation?
Automation is a broad term applied to any mechanism that moves by itself. It describes a wide range of technologies, methods, and tools used to reduce human intervention.
Industrial automation is a field that primarily involves automating industrial processes and machinery to reinforce manufacturing, material handling, and quality control processes.
The initial purpose of automation was to increase productivity and reduce labor costs. Nowadays, automation has shifted to minimizing error and improving quality and flexibility in a manufacturing process.
McKinsey's report in 2018 has already shown that automation is a global phenomenon occurring across regions and industries. The same survey repeated in 2020 showed that 66% of organizations are at least adopting automation in one or more business units, growing from 57% in 2018. Moreover, nearly half of companies that have not begun to automate will plan to do so within the following year. The industrial automation market is projected to reach USD 414.48 billion by 2030
McKinsey further reported the most common technology deployed in automation are business-process-management platforms and robotic process automation. These are followed by image-recognition technologies, such as optical character recognition (OCR), and by machine-learning algorithms and automated process-mining, -discovery, and -documentation tools.
From the steam engine to the smart factory
Automation is an integral part of the industrial revolution. Although the buzz around automation emerged in the 20th century, it has existed long before that. Through steam power and mechanization of production during the first industrial revolution, several automation solutions emerged in the market, such as water-powered automated spinning mills, automated looms, and automated flour mills.
The second industrial revolution was marked by the adoption of electricity and assembly line production that made mass production possible for the automotive industry. Henry Ford was one of the pioneers in this field, establishing an automation department in 1947 as part of its operations.
The third industrial revolution is also known as the digital revolution. The spread of automation and digitization characterizes it by the use of electronics and computers, the invention of the Internet, and the discovery of nuclear energy.
The fourth industrial revolution is the buzzword of today. Also known as Industry 4.0, this era is marked by the wide adoption of multiple technologies that are part of the automation field. Building from technological advancement achieved in third industrial revolution, Industry 4.0 expands the production system to include large scale digitalization, IoT networks, machine learning, AI, Big Data, cloud computing, and advanced robotics. This allows communication between processes, functions, and devices that takes us to the next level of automation in which production is nearly autonomous, also known as the smart factory.
In this new era, manufacturing facilities are digitalized making them smart factories where all the systems are integrated to make factories to be fully automated and fully connected. The combination of cloud computing, IoT, and advanced analytics enables factories to be flexible by learning and adapting in real time.
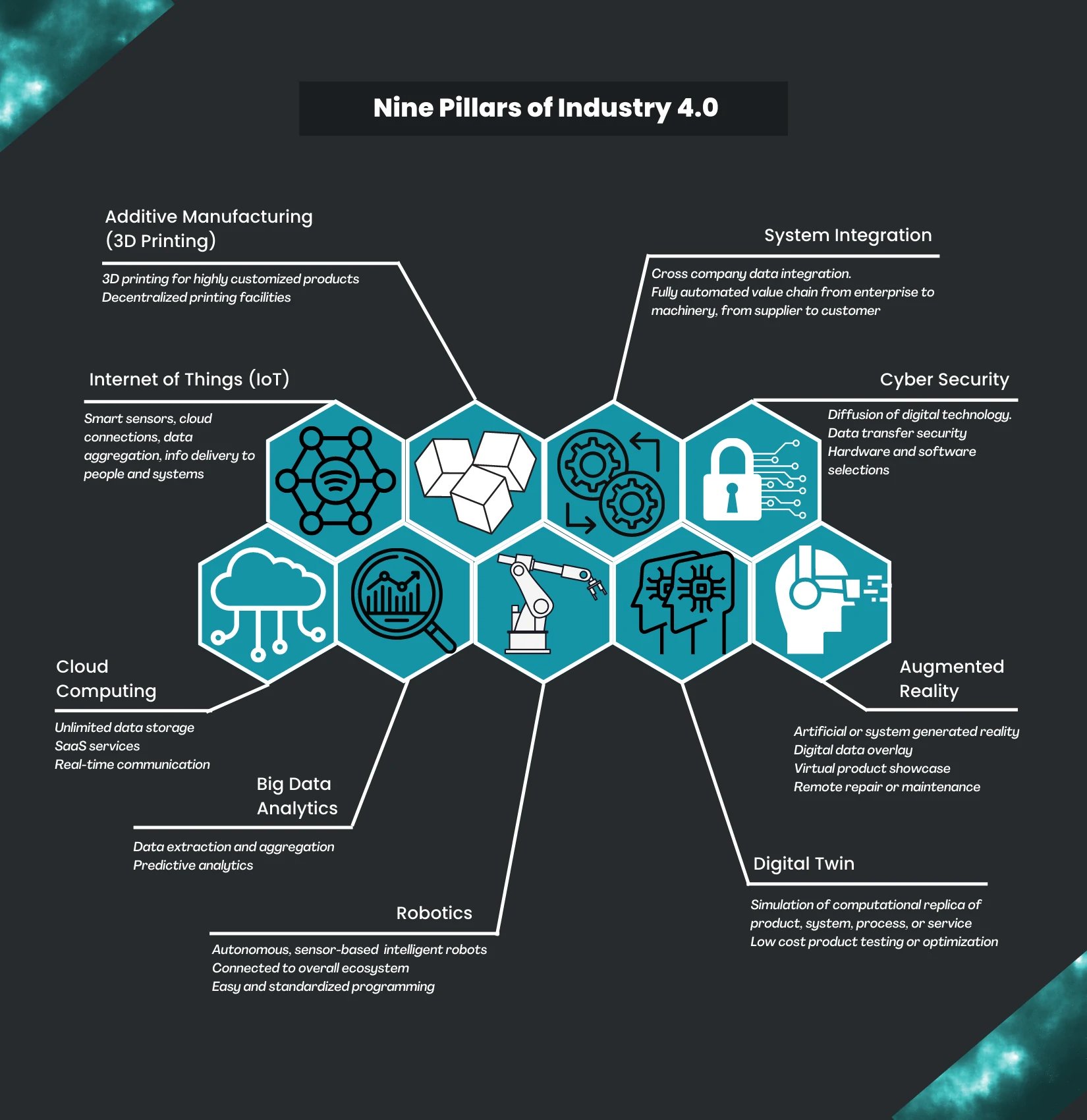
The nine pillars of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 create describes a future state of a fully digitalized industrial economic and production flows with the basic objective of creating faster, more flexible, and efficient processes. It is built on 9 pillars of technological advancements that connect the physical and digital worlds that enable autonomous and intelligent systems. These 9 pillars are additive manufacturing, system integration, IoT, cyber security, cloud computing, augmented reality, big data analysis, digital twin technology, and robotics.
How Industry 4.0 changes businesses
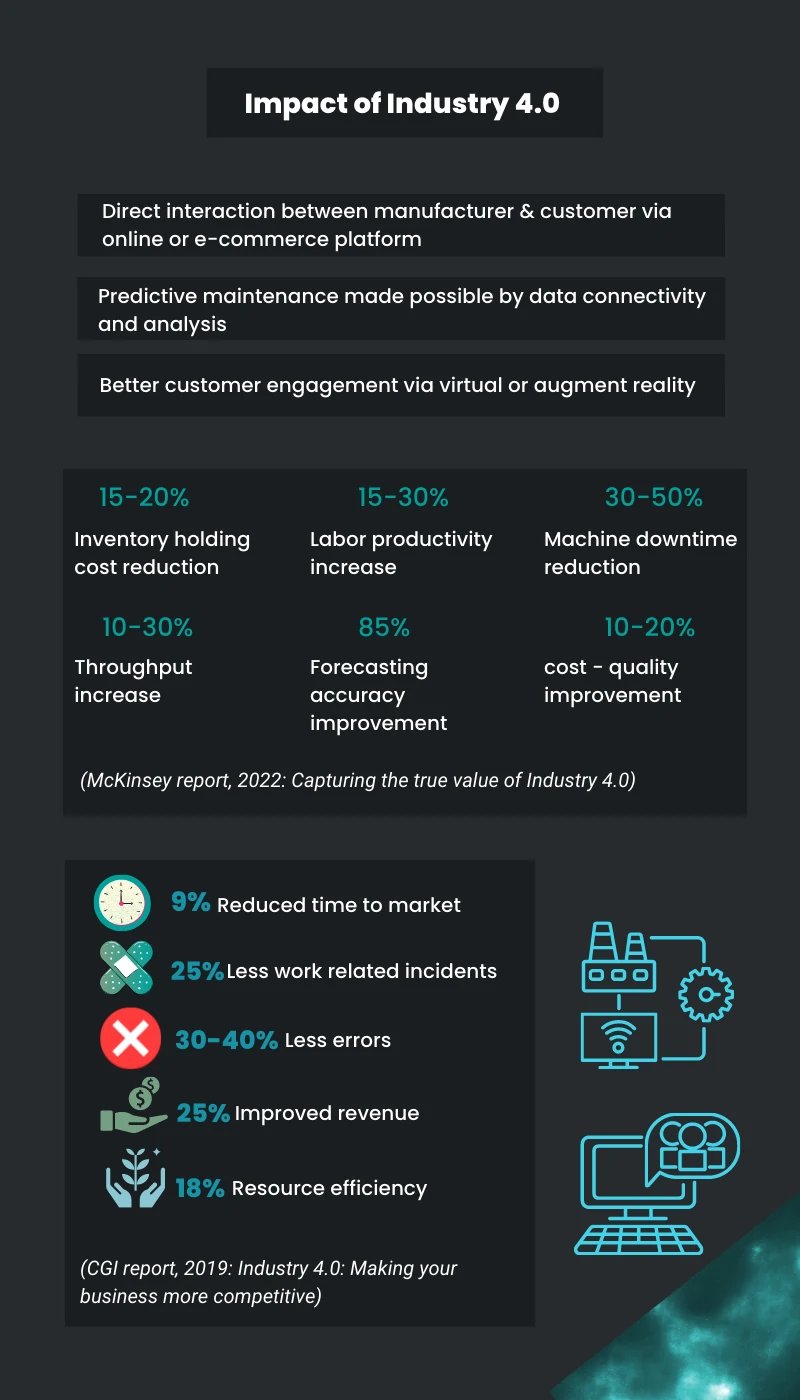
Businesses are in a new industrial era that’s transforming traditional values in manufacturing. Industry 4.0 provides the opportunity for companies to be responsive to customers in ways traditional manufacturers can't do. Through big data, augmented reality (AR), and cloud computing they can respond immediately to customer demands in a short lead time.
How Industry 4.0 changes the way we work
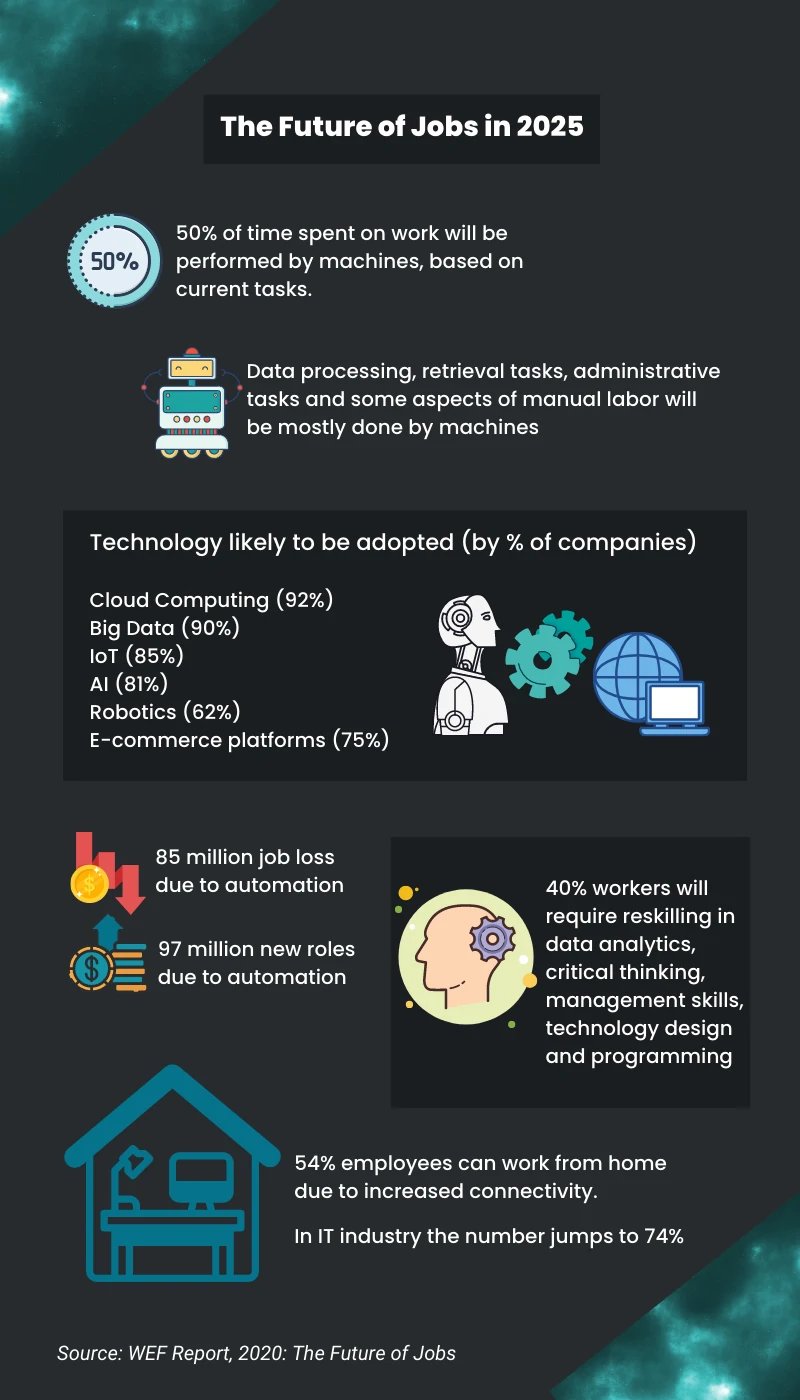
Technology combined with employees’ needs and demands are shaping the nature of work. Although technology advancement is often associated with job loss, it also creates new roles that never existed before. This shift in roles and tasks requires both companies and employees to adapt by learning a new subset of skills and knowledge. Reskilling in data analytics, critical thinking, technology design, and programming are some of the essential requirements that need to be done in the industry 4.0 era.
Trends driven by Industry 4.0
Sustainability is a big trend that will be pushed further in the industry 4.0 era. Smart factories will push a trend of lowering the amount of energy used to manufacture products. This will not only result in a lower cost of production but it also aims at reduced emission.
Customized product at a mass-produced price is another trend that currently flourishing thanks to generative design technology and big-scale automation with the help of robots. Product customization is a way for companies to respond to customer demands that are now possible to be done massively.

Sources:

