While electric cars for personal use have gained significant attention and market share in recent years, there is now a growing emphasis on electrifying commercial vehicles. The transition to electric mobility in commercial vehicles is seen as a crucial step in achieving overall transportation sustainability and reducing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
Just like with electric passenger cars, the light commercial vehicle (LCV) category has witnessed a rising trend in new registrations of electric vehicles in recent years.
LCVs are commonly used in commercial fleets, and this widespread adoption can positively influence the uptake of EVs in various ways. The lower total cost of ownership and operating expenses are strong reasons for fleet managers to consider electric LCVs over traditional ICE vehicles. Fleet managers have an advantage over private users as they can accurately predict their vehicles' movements. This capability allows them to efficiently manage range limitations and charging schedules.
Global Electric LCV Market Size
As per IEA's latest Global EV Outlook report, in 2022, electric LCV sales worldwide saw an impressive increase of nearly double compared to 2021, totaling over 310,000 vehicles. Globally, electric LCVs now make up 3.6% of the total LCV sales share. It is also important to note that for the first time in 2022, the increase in the share of electric LCVs outpaced that of electric passenger cars (albeit from a low base).
As per IEA's latest Global EV Outlook report, in 2022, electric LCV sales worldwide saw an impressive increase of nearly double compared to 2021, totaling over 310,000 vehicles. Globally, electric LCVs now make up 3.6% of the total LCV sales share. It is also important to note that for the first time in 2022, the increase in the share of electric LCVs outpaced that of electric passenger cars (albeit from a low base).
Around 98% of both electric LCV sales and stock in 2022 were BEVs and the rest 2% were PHEVs.
In terms of market value, Market Research Future reports that the global light commercial vehicle market was valued at USD 8.9 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach USD 56.6 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 26%.
Regional Dynamic of the e-LCV Market
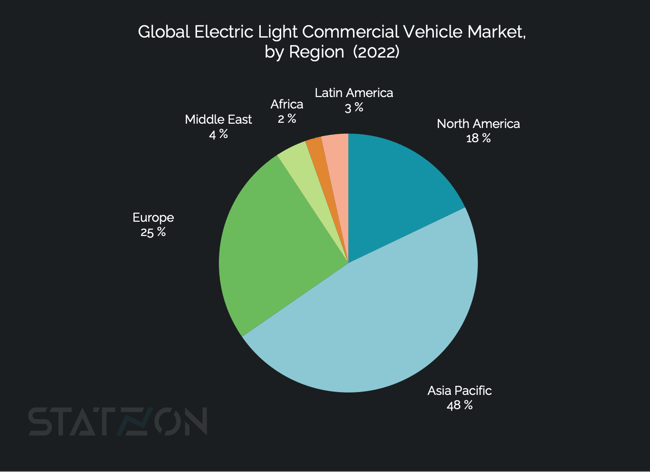
Asia-Pacific is leading the market, controlling 48% of the global electric LCV market. Asia Pacific is expected to dominate until the end of the projection period in 2030. Europe and North America are in the next position with shares of 25% and 18% respectively. At the same time, developing countries such as India and China are projected to showcase substantial growth throughout the forecast period.
 Source: Statzon/ Market Research Future
Source: Statzon/ Market Research Future
Similar to the passenger car category, China dominates the electric LCV market, earning USD 2.1 billion in 2022. With a projected growth rate of 21.4% CAGR, China's market is expected to reach USD 13.4 billion by 2030. The US follows as the second highest revenue-generating country, reaching USD 1.2 billion in 2022. Europe, as a whole, generated approximately USD 2.2 billion, with Germany emerging as the largest market in the region.
Despite a decrease in subsidies for battery electric and fuel cell trucks and vocational vehicles, in China, the sales of zero-emission commercial trucks have been on the rise since 2020. In 2022, China took the lead in overall electric LCV sales, with over 130,000 units sold, accounting for nearly 15% of all LCVs sold being electric.
Growth is expected to continue across all regions. Based on McKinsey's analysis, growth in the LCV market is primarily driven by three key trends: the increasing focus on last-mile delivery, propelled by the continuous expansion of e-commerce; the sustained growth in e-grocery, and the rising demand in the recreational-van market, particularly in Europe, where LCV platforms serve as the base vehicles for these vehicles.
Declining prices of electric vehicle components are likely to happen and will further boost the adoption of electric light commercial vehicles. Over the next few years, the powertrain cost per vehicle for commercial vehicles is anticipated to see a significant decline. According to data from Interact Analysis, the average cost of the powertrain for an electric light-duty truck was over USD 9,000 in 2021. However, projections indicate that by 2030, it is expected to decrease significantly by 56%, reaching just over USD 5,000. 
e-LCV Market Segmentation
Commercial vehicles have a wider range of uses compared to personal vehicles, making their EV-related needs, like battery size and range, more diverse. The intended purpose of a light commercial vehicle significantly impacts its requirements.
The global e-LCV market has been categorized by Market Research Future into segments such as facility management, last-mile delivery, industrial, agricultural, and others. Among these segments, the last-mile delivery segment is projected to experience substantial growth at a rate of 25.5% during the forecast period. In 2022, the passenger car segment accounted for 34.8% of the total global electric light commercial vehicle market.
This is in line with predictions from McKinsey that segmented the market into ten core categories that include recreational vehicles, rental vehicles, miscellaneous services industries, trade and groceries, construction, logistics, manufacturing, municipal, passenger transport, and other private applications and use.
Based on McKinsey's analysis, the RVs and passenger transport segments are experiencing rapid growth. RVs have shown steady growth over the past few years and are now the largest LCV segment in Europe, a trend expected to continue in the coming decade. Although passenger transport is a smaller segment, it is projected to increase along with the growth of ride-sharing models. The next-fastest-growing segments are the trade & grocery segment and the logistics segment. In the trade segment, the grocery share is still rather small. However, the trend of ordering fresh food online with the fastest possible delivery. The same applies to CEP and logistics, for which the home delivery market is expected to continue growing as tech-enabled retail supergiants focus on the last-mile delivery market. 
Electric LCV TCO Parity
When it comes to the expected timing of total cost of ownership (TCO) parity for electric LCVs, two important factors play a significant role: battery size and the estimated annual mileage or how much the vehicle will be used throughout the year. These factors contribute to when electric LCVs become financially competitive with conventional vehicles in terms of overall costs.
Analysis of costs of ownership presented by this study indicates that small electric LCVs are already as cost-effective as conventional ones. However, medium and large electric LCVs have slightly higher ownership costs, amounting to EUR 1,200 and 2,300 (around USD 1,300-1,400 in today's conversion rate) over a five-year period. Nevertheless, this difference is often offset by financial incentives available in many European countries.
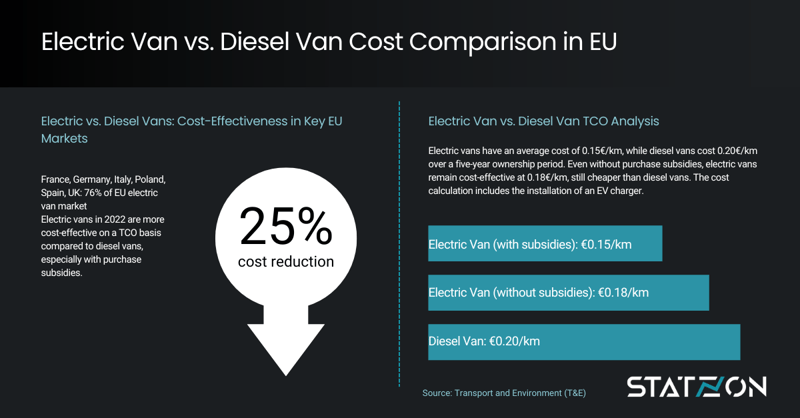
A study by Transport and Environment (T&E) concluded that the EU electric van is 25% cheaper than the average diesel van when subsidies are considered.
In six European countries, representing 76% of the EU+UK electric van market, electric vans bought in 2022 are more cost-effective on a TCO basis than their diesel counterparts, especially when purchase subsidies are factored in. On average, with a cost of 0.15€/km for the e-van compared to 0.20 €/km for the diesel van over a five-year ownership period. Even if purchase subsidies are not included, owning an electric van would cost 0.18€/km, which is still cheaper than owning a diesel van. The installation of an EV charger is already accounted for in the cost calculation.
However, LCV is a broad term that includes many types of vehicles. McKinsey understands this by doing a TCO analysis for several types of vehicles.
In their analysis, electric delivery vans already reach total cost of ownership (TCO) parity with ICE vans within the first year of use. Within two years, the electric version gains a 10% cost advantage over its ICE counterpart. This is made possible because delivery vans are used for many short trips on a daily basis, resulting in a high annual mileage of around 35,000 km, while utilizing a relatively small battery with a 60 kWh capacity.
Another TCO comparison was conducted for recreational vans, which are expected to travel long distances and require batteries of 140 kWh or more. However, since these camper vans are not typically driven daily, their annual mileage is low. As a result, TCO parity for recreational vans is projected to be achieved only within the next 8 years. 
Latest e-LCV Sales Trends
In Europe, as reported by ACEA, the first half of 2023 saw diesel vans maintain their position as the top choice, albeit with a slight decrease in market share to 83.5% from 87.2% in 2022. However, there's a noticeable uptick in the popularity of alternative powertrains, with electrically chargeable vans witnessing a remarkable two-fold increase (+100.4%), reaching 6.9% market share. This growth is primarily attributed to substantial increases in France (+118.9%) and Spain (+138%).
Moreover, Interact Analysis highlights the impressive growth of new energy commercial vehicles (NECVs) in China. Registrations of NECVs, including battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), surged by 62.0% year-on-year in the first three quarters of 2023, reaching 199,000 units. Light-duty commercial vehicles, particularly light-duty trucks, have been driving this momentum, capturing a significant share of the market and experiencing substantial year-on-year growth. Additionally, small-sized buses saw record-high sales, doubling in registrations compared to the previous year and dominating the new energy bus market.
Looking ahead, the Bloomberg NEF Electric Vehicle Outlook 2023 projects a significant surge in global electric vehicle (EV) sales, driven by favorable economics, an expanding range of available models, increasing fleet commitments, and supportive city policies. By 2040, e-LCV sales are projected to constitute nearly 70% of global EV sales, with China leading the charge.

Sources: Statzon, Market Research Future Report on Electric LCV, Science Direct, McKinsey, IEA, Interact Analysis, Transport & Environment , ACEA, Bloomberg NEF, Interact Analysis (2),

_2022.png?width=650&height=471&name=Chart_World_Share_of_Electric_Vans_of_the_Total_Van_Sales_(Percent)_2022.png)